Ram is not directly put on the CPU because if you do so, there is a great chance to burn out the RAM chip.
RAM is designed with silicon wafers that are not suitable for the CPU because there is a great chance that the processor is heating up after some time.
The construction process of both RAM and CPU is very different, If you want to fix the RAM in the CPU, you have to change the manufacturing process of RAM.
And the new RAM that is fixed in the CPU is quite expensive. Many people cannot afford it.
The benefit of using separate RAM and CPU is that you can upgrade both parts of the computer easily, If you want to increase your RAM you can individually change the RAM, you do not need to change the whole CPU or make any change in the processor.
While several experimental designs have tried to combine CPU and RAM technology, these designs have their difficulties and trade-offs.
Due to its adaptability, scalability, and compatibility with current systems, the separation of CPU and RAM continues to be the preferred design strategy. So it is beneficial that RAM is not put in the CPU.
How to measure CPU performance?
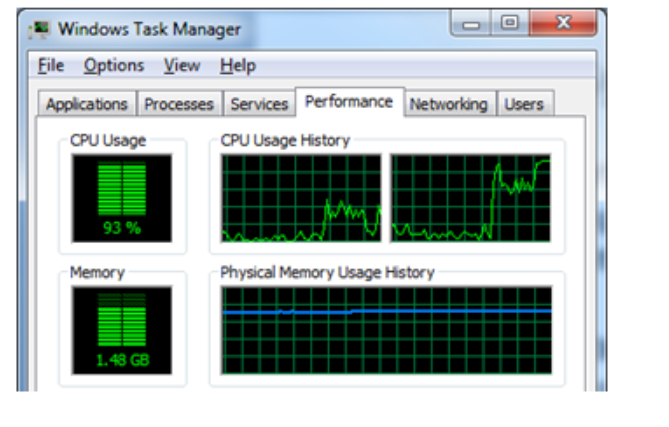
Various methods are used to measure the performance of the CPU. Some standard methods are discussed below:
Clock Speed:
A CPU’s clock speed, expressed in gigahertz (GHz), describes how many cycles it can process in a second.
However, measuring the performance of the CPU depends upon the clock speed because it is the major factor among all other things.
Analysing Software:
On the benchmark level, there are various tools which are named a CPU gauge, used to measure the performance of the CPU.
To compare performance, these tools replicate real-world circumstances and produce scores or ratings. These programs Geekbench, PassMark, and Cinebench are well-known.
Synthetic Benchmarks:
To measure the performance of the CPU in a controlled environment, synthetic benchmarks are designed. These are used to measure the accurate performance and efficiency of the CPU.
Examples of artificial benchmarks include Prime95 for CPU stress testing and 3DMark for graphics performance.
Generally, to check the performance of the CPU, you can perform several tasks and make a load on the CPU, If the processor is not working properly you need to upgrade it. Otherwise, it is the best for your work.
How to measure RAM performance?
The performance of RAM (random access memory) depends upon various factors and tools. Here are some methods to measure the performance of RAM.
Memory Bandwidth:
Memory bandwidth quantifies the volume of data that can be moved into or out of RAM in a predetermined amount of time.
Generally, performance is measured in gigabytes per second. If the bandwidth value is high, it means that your RAM is in excellent condition.
Throughput:
The pace at which data may be read from or written to the RAM is referred to as RAM throughput. The units of measurement are megabytes per second or gigabytes per second.
There are two programs named MemTest86 and AIDA64, which many programmers used to gain information about RAM throughput.
Latency:
RAM takes a few moments to reply to a memory request, this period is known as RAM latency. This period is measured in clock cycles or nanoseconds. If you receive fast replies, it means that the latency value is low. MemTest86 and CPU-Z, are two programs used for the RAM latency.
Applications in the real world:
Running memory-intensive programs or tasks while keeping an eye on their performance might give you useful knowledge about RAM performance.
Some applications for example are data processing, gaming, and video editing. You can check the RAM performance by considering the speed of these applications.
To make sure the RAM is operating as intended, it might also be important to compare the findings to the RAM module’s specs (such as the advertised speed, latency, and bandwidth).
How Are My CPU and RAM Going to Work Together?

In every computer system, RAM and CPU are separate things but work together to perform various tasks and functions.
CPU is the computer’s brain system. It executes commands and performs calculations, making it in charge of the system’s entire processing power.
It helps to carry out all the functions and operations that are stored in the computer’s memory.
On the other hand, RAM is a temporary storage device. It helps to access data rapidly. It gives the CPU a location to keep and access data that is currently being used.
Compared to the computer’s hard disc or solid-state drive (SSD), which is utilized for long-term storage, RAM is accessed more quickly.
Above all, the CPU performs tasks and operations that are stored in the RAM. The speed at which information is exchanged between the CPU and memory can be enhanced by faster RAM. By all the statements, it is clear how the RAM and CPU work.
Conclusion: Why is RAM not put on the CPU chip?
By considering all the points mentioned above, it may be clear to you why RAM is not put in the CPU. The main reason for using separate RAM is to prevent the RAM from burning.
Another thrilling benefit of using separate RAM is that you can easily upgrade the RAM without making any changes to the CPU. Overall, It is very beneficial to use separate RAM and CPU.